There are now two manufacturing processes, JS 3D printing & injection molding, that provide precision, speed, & flexibility. 3D printing manufactures parts by adding each layer, whereas injection molding manufactures durable, multiple-shaped parts with flowing molten material. Both manufacturing technologies allow smart solutions for rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing.
Wondering how ideas are manufactured into real parts in minutes? JS 3D Printing and Injection Molding provides speed, shape, and strength to meet excellent precision in manufacturing to realize design ideas in the physical world. Explore why JS 3D printing and injection molding are the modern methods that will define the function of smart manufacturing for years to come.
JS 3D printing and injection molding are two powerful ways to manufacture parts. Prototyping is a great method to use when challenging your designs, but injection molding works better for volume production; this ability merges creativity with precision and speed for today’s modern manufacturing attributes.
What is JS 3D printing?
In JS 3D printing, there are additives employed by which the materials can be printed separately, creating 3D objects layer upon layer using various other materials, like plastic, resin, or metal, through the printer. JS typically refers to a general process or trade name in reference to an exclusive yet high-end value of 3D printing materials or services. This method is called additive manufacturing or 3D printing, which turns the images of digital models in three dimensions into objects by directly depositing the required material to create them.
What is the JS 3D process to print?
This JS three-dimensional printing process is always initiated with the help of a digital 3D model produced with CAD.
- Slicing: Cutting the model into thin, horizontal slices using a slicing application.
- Printing: The process of the JS 3D printer “printing” the object’s horizontal layers.
- Post-Processing: After all of the printing activities are concluded, the object may continue having to be cleaned, cured, or finished.
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is the traditional sort of manufacture that makes parts, every part being identical, at the same time. Injection molding is the process of injecting liquid material into a mold cavity and cooling it down to harden it.
JS 3D Printing vs. Injection Molding: What You Need to Know
Both JS 3D printing and injection molding processes produce physical components; however, they differ sharply in processes, costs, times, and use cases. What is 3D printing?
JS 3D Printing vs. Injection Molding
Aspect JS 3D Printing Injection Molding
Production Method Additive (builds layers one at a time) Subtractive/Molding (using molds)
Setup Cost Low (no need for molds) High (creating molds is expensive)
Production Speed: Slower for Mass-Metal Production; Very Rapid for Mass Production: Complexity: complex, custom-designed; best for simple, repetitive parts Cost-effective—Very Economical Small Batches; Cost-effective for Mass Production
Why are JS 3D Printing & Injection Molding Important on a Global Scale?
1. Rapid Prototyping and Product-Development
The most important meaning of JS 3D Printing and Injection Molding for the global community is rapid prototyping and product development; it lets amazing doors open for designers and engineers to prototype and try out concepts much more quickly and at a fraction of the cost. Rapid prototyping contributes to decreasing the product development cycle through allowing for fast testing and improvement before putting money into expensive and time-consuming molds.
2. Precise Mass Production
Injection molding is a vital process to mass-produce a consistent and high-quality part with the utmost efficiency. It’s extremely essential in high-volume manufacturing of automotive parts, consumer electronics, medical devices, etc.
3. Customization Meets Scale
A combination of JS 3D printing for prototyping & injection molding for production allows businesses to have the best of both worlds. It allows businesses to develop and customize products for their specific needs, then produce the goods at scale.
4. Cost efficiency and waste reduction
JS 3D printing uses only the material necessary to print the object, reducing material waste.
Injection molding can lower labor costs with automation and waste less material than more traditional methods of manufacture.
Advantages of JS 3D Printing
Flexibility of Design: Can achieve complex geometries and/or very detailed features.
Turnaround Time: Very suitable for prototypes or small batch production.
Tooling: No molds or tooling, so no expensive tooling costs required.
Customization: Each product can be customized at no charge.
Materials: Capable of using only one or multiple materials. Typically incorporates specialized polymers or metals.
Pros of Injection Molding
- Uniform Quality and Accuracy: No deviation from the guide has ever created the same type of part.
- Durability: Parts produced are sturdy and can be functional.
Applications within industries
Medical
- Custom prosthetics and surgical knives in 3D printing.
- Millions of identical mass-produced medical devices and components in injection molding.
Automotive
- Fast prototype of parts in 3D printing.
- Millions of robust interior and exterior components in injection molding.
Why JS 3D Printing is Important
- Speed and Flexibility: From a cost and risk standpoint, you never have to wait for tooling delays because you can make design changes on demand.
- Cost-Efficient for Small Runs: For small runs, small runs do not involve the expensive cost of making molds.
- Creativity in Design: Customers can make shapes through this platform that traditional ways cannot.
- Sustainable Production: Produces less material and energy waste than subtractive methods.
- Facilitates Innovation: JS 3D printing provides additional chances to test experimental product designs and allows for immediate iteration.
- Customization/Personalization: The only expense of producing based on an individual is the same cost. JS 3D printing allows production based on individual needs without the burden of additional cost.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: This allows for parts to be produced on demand, leading to the opportunity to reduce inventory and storage costs.
- Global Production Opportunities: This technology enables local production opportunities anywhere in the world.
Challenges and Considerations
Both JS 3D printing and injection molding are powerful assets for manufacturers, but neither comes without some challenges.
- 3D Printing Speed: Not a viable option when doing a very large production run.
- Material limitations: Some materials are made specifically for injection molding.
- Costly initial investment: Injection molding requires a large investment up-front on mold cost.
The Future of Manufacturing: JS 3D Printing and Injection Molding
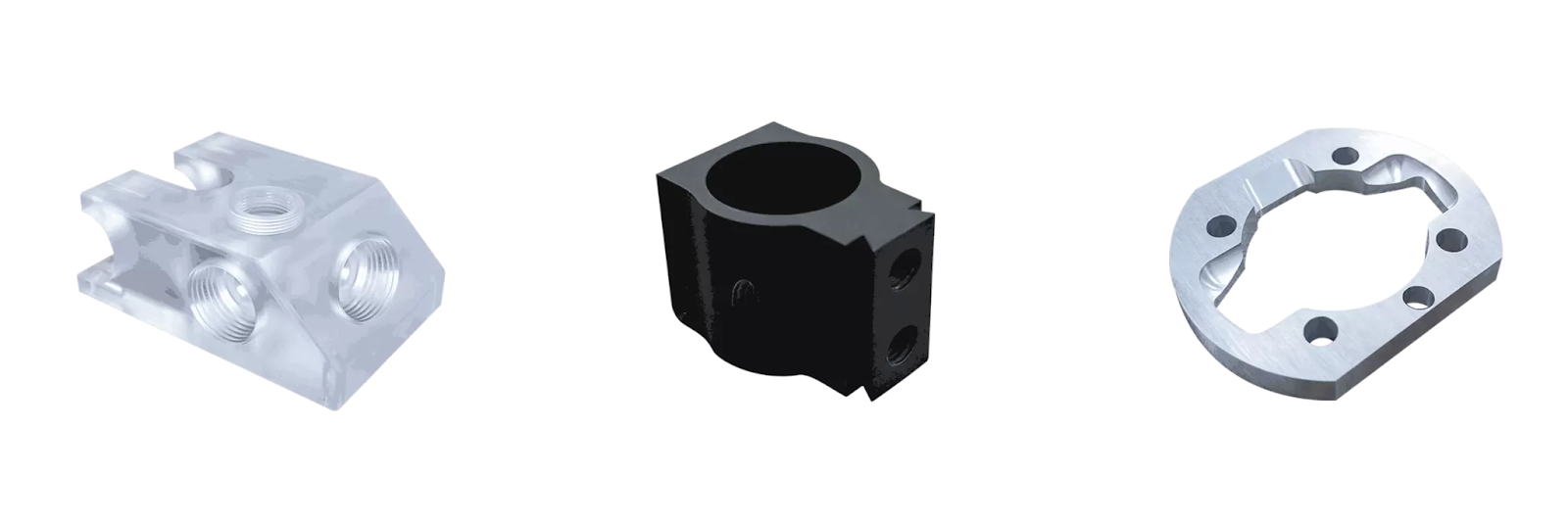
I believe we will see more hybrid options that take advantage of each technology’s strengths. 3D printing is typically used to produce prototype molds or custom limited-run parts, and injection molding is a technique for mass production. As improvements in materials, automation, and software are made, the applications for both of these processes will only get better.
Companies that leverage these technologies today will be better positioned to meet the demands of a changing, global market of manufacturing.
Conclusion
JS 3D printing and injection molding are both very important to modern manufacturing processes. Understanding the differences and advantages of using both processes and how they work together to truly add value to businesses and manufacturing across all verticals in every part of the world is valuable. Be it product quick prototyping or mass production, both processes are changing and are moving forward with the design, manufacture, and delivery of the products. The commencement of JS 3D printing and injection molding capability would not only mean more efficiency at a lesser cost but would also allow innovation and sustainability backing.
FAQs:
1: What is the difference between JS 3D printing and normal 3D printing?
JS 3D printing generally has less tolerance, better material performance, and speed of giving CAD to print. It is intended for high detail for small-batch production.
2: Why use both 3D printing and injection molding?
Both allow for the rapid transition from prototypes via 3D printing to actual mass production by way of injection molding, thus saving time and reducing costs.
3: Is JS 3D printing better for long-use products?
Yes, especially with strong materials—JS 3D printing can provide durable, functioning components for real-life deployment.



